Stability of carbonium ions :-
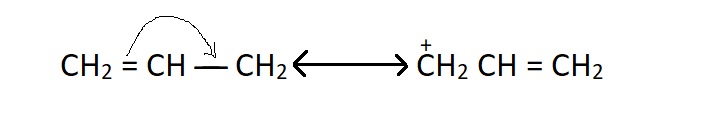
This is influenced by both resonance and inductive effects. For example, the allyl and benzyl carbonium ion can be stabilized by resonance as shown below but propyl carbonium ion (CH3CH2CH2 +) ha no resonance.
Resonance forms of allyl carbonium ions :
Electron releasing groups (+I Groups) also stabilize carbonium ions by partial neutralization of the positive charge on carbon.
Thus a tertiary carbonium ion is more stable than a secondary, which is turn in more stable than a primary because of the +I effect associated with alkyl groups.
The stability of carbanions is also influenced by resonance and inductive effects. For example, the benzyl carbanion is much more stable than propyl carbanion. This is because the benzyl carbanion can be stabilized by resonance propyl carbanion (CH3CH2CH2 -) has no resonance forms.
Stabilization of carbanions by inductive effect in the opposite direction from the carbonium ions. electron releasing groups (+I groups) make the carbanions less stable. Thus a primary carbanion is more stable than a secondary, which in turn is more stable than a tertiary because of the +I effect associated with alkyl groups.
Electron attracting groups (-I groups) like NO2, Br will stabilize carbanion by partial removal of the negative charge on the carbon.
Puvvukonvict......................











0 Comments
Thanks for your feedback, ll get back to you soon