Electrophilic substitution of benzene
Nitration, Acylation, Sulphonation
Nitration :-
Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid at 60° C to form nitro benzene.
Mechanism :-
Step1 : Formation of the electrophile (NO2+)
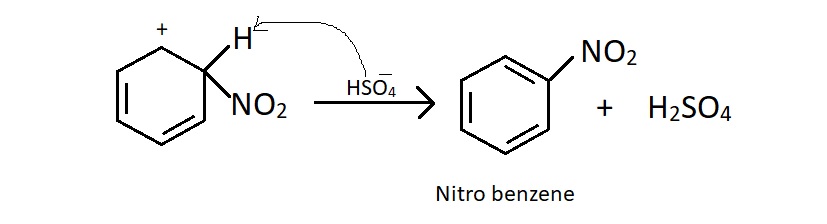
Step2 : The electrophile attacks the benzene ring to form a carbonium ion.
Step3 : Loss of proton yields nitro benzene.
Benzene reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid at 120° C or fuming sulphuric acid at room temperature to give benzene sulphonic acid.
Note:- Fuming sulphuric acid is concentrated sulphuric acid that contains added sulpher trioxide.
Mechanism :-
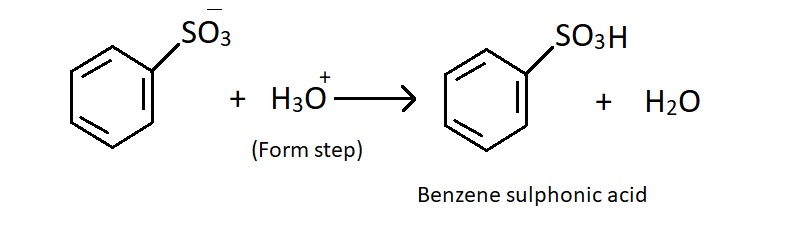
Step1 : Electrophile is formed in this reaction the electrophile is sulphur trioxide (SO3). In concentrated sulphuric acid, SO3 is produced as follows. in fuming sulphuric acid, this step is not important because the dissolved SO3 reacts directly.
Step3 : Loss of proton.
Acylation :-
Benzene reacts with acid chlorides or anhydrides in the presence of aluminium chloride to give aromatic ketones.
Step1 : Formation of the electrophile (CH3 – C+ = O)
Puvvukonvict......................
























0 Comments
Thanks for your feedback, ll get back to you soon